START-UP INDIA
1) Start-up India
Start-up
India
campaign is based on an action plan
aimed at promoting bank financing for start-up ventures to boost
entrepreneurship and encourage start-ups with jobs creation. The campaign was
first announced by Prime Minister Narendra Modi in his 15 August 2015 address
from the Red Fort. It is focused on to restrict role of States in policy domain
and to get rid of "license raj and hindrances like in land permissions,
foreign investment proposal, environmental clearances. It was organized by
Department of Industrial Policy and Promotion (DIPP). A start- up is an entity
that is headquartered in India which was opened less than five years ago and
has an annual turnover less than Rs. 25 crore (US$3.7 million). The government
has already launched iMADE, an app development platform aimed at producing
1,000,000 apps and PMMY, the MUDRA Bank, a new institution set up for
development and refinancing activities relating to micro units with a refinance
Fund of Rs. 200 billion (US$3.0 billion).
The
Stand-up India initiative is also aimed at promoting entrepreneurship among
SCs/STs, women communities. Rural India's version of Start-up India was named
the Deen Dayal Upadhyay Swaniyojan Yojana. To endorse the campaign, the first
magazine for start- ups in India, The Cofounder, was launched in 2016.
Key Points
·
Single Window Clearance even with
the help of a mobile application
·
10,000 crore fund of funds
·
80% reduction in patent registration
fee
·
Modified and more friendly
Bankruptcy Code to ensure 90-day exit window
·
Freedom from mystifying inspections
for 3 years
·
Freedom from Capital Gain Tax for 3
years
·
Freedom from tax in profits for 3
years
·
Eliminating red tape
·
Self-certification compliance
·
Innovation hub under Atal Innovation
Mission
·
Starting with 5 lakh schools to
target 10 lakh children for innovation programme
·
New schemes to provide IPR
protection to start-ups and new firms
·
Encourage entrepreneurship.
·
Stand India across the world as a
start-up hub
Government Role
The
Ministry of Human Resource Development and the Department of Science and
Technology have agreed to partner in an initiative to set up over 75 such
start-up support hubs in the National Institutes of Technology (NITs), the
Indian Institutes of Information Technology (IIITs), the Indian Institutes of
Science Education and Research (IISERs) and National Institutes of
Pharmaceutical Education and Research (NIPERs). The Reserve Bank of India said
it will take steps to help improve the ???ease of doing businesses in the
country and contribute to an ecosystem that is conducive for the growth of
start-up businesses
Action Plan
Start-up
India:
The Prime Minister of India, Shri
Narendra Modi had this year in his Independence Day speech announced the
???Start-up India??? initiative. This initiative aims at fostering
entrepreneurship and promoting innovation by creating an ecosystem that is
conducive for growth of Start-ups. The objective is that India must become a
nation of job creators instead of being a nation of job seekers. The Prime
Minister of India will formally launch the initiative on January 16, 2016
from Vigyan Bhawan, New Delhi. The event will be attended by a vast number of
young Indian entrepreneurs (over 2000) who have embarked on the journey of
entrepreneurship through Start-ups.
As a key component of this ???Start-up India??? launch, Government of India is organizing a global workshop on ???Innovation and Start-ups??? on January 16, 2016 . Shri Narendra Modi, Prime Minister of India will be the Chief Guest on the occasion. This workshop aims to provide a platform to bring together all stakeholders, stimulate dialogue on key challenges that the Indian innovation ecosystem currently faces, and provide the potential solutions to address them. Fostering a fruitful culture of innovation in the country is a long and important journey. This initiative will go a significant way in reiterating Government of India???s commitment to making India the hub of innovation, design and Start-ups.
START-UP INDIA
2) Steps to Starting
a Business
Starting a business involves planning, making key
financial decisions and completing a series of legal activities. These 10 easy
steps can help you plan, prepare and manage your business. Click on the links
to learn more.
Step 1: Write a Business Plan
Use these tools and resources to create a
business plan. This written guide will help you map out how you will start and
run your business successfully.
·
Define
your vision:
What will be the end result of your business?
·
Define
your mission:
Different to a vision, your mission should explain the reason your company
exists.
·
Define
your objectives:
What are you going to do -- what are your goals -- that will lead to the
accomplishment of your mission and your vision?
·
Outline
your basic strategies:
How are you going to achieve the objectives you just
bulleted?
·
Write a
simple action plan:
Bullet out the smaller task-oriented actions required
to achieve the stated objectives.
Step 2: Get Business Assistance and
Training
Take advantage of free training and counselling
services, from preparing a business plan and securing financing, to expanding
or relocating a business.
Step 3: Choose a Business Location
Get advice on how to select a customer-friendly
location and comply with zoning laws.
Step 4: Finance Your Business
Find government backed loans, venture capital and
research grants to help you get started.
Step 5: Determine the Legal Structure of
Your Business
Decide which form of ownership is best for you:
sole proprietorship, partnership, Limited Liability Company (LLC), corporation,
S corporation, non-profit or cooperative.
Step 6: Register a Business Name
("Doing Business As")
Register your business name with your state
government.
Learn which tax identification number you'll need
to obtain from the IRS and your state revenue agency.
Step 7: Register for State and Local Taxes
Register with your state to obtain a tax
identification number, workers' compensation, unemployment and disability
insurance.
Step 8: Obtain Business Licenses and
Permits
Get a list of federal, state and local licenses
and permits required for your business.
Step 9: Understand Employer
Responsibilities
Learn the legal steps you need to take to hire
employees.
Step 10: Find Local Assistance
Contact your local SBA office to learn more about how SBA can help.
START-UP INDIA
3) Start-up Resources
There are a number of available programs
to assist start-ups, micro businesses, and underserved or disadvantaged groups.
The following resources provide information to help specialized audiences start
their own businesses.
·
Environmentally-Friendly
"Green" Business
·
Home-Based
Business
·
Online
Business
·
Self-Employment
·
Minority
Owned Business
·
Veteran
Owned Business
·
Woman
Owned Business
You can save money when starting or
expanding your business by using government surplus. From commercial real
estate and cars, to furniture, computers and office equipment, find what you
need for your business in one place any entrepreneurs were excited by the
announcements made by Prime Minister Narendra Modi as part of the start-up
India Action Plan. There is no doubt the measures were significant, but they do
beg the question, are all the start-ups really eligible for the benefits that
were announced?
Here is a quick analysis of the eligibility
criteria
(please note that the following flow chart is specifically
applicable for start-ups seeking tax exemption):
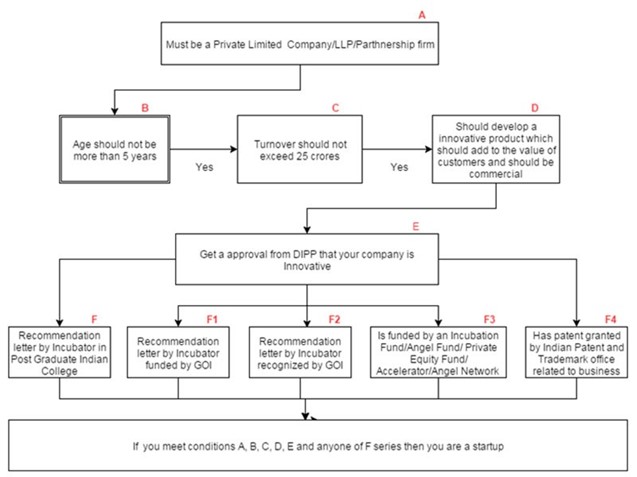
In addition, for a start-up to be
recognized as one,
1.
It
must be an entity registered/incorporated as a:
o
Private Limited
Company under the Companies Act, 2013; or
o
Registered
Partnership firm under the Indian Partnership Act, 1932; or
o
Limited Liability
Partnership under the Limited Liability Partnership Act, 2008.
2.
Five
years must not have elapsed from the date of incorporation/registration.
3.
Annual
turnover (as defined in the Companies Act, 2013) in any preceding financial
year must not exceed Rs. 25 crore.
4.
Start-up
must be working towards innovation, development, deployment or
commercialisation of new products, processes or services driven by technology
or intellectual property.
5.
The
start-up must aim to develop and commercialise:
o
a new product or
service or process; or
o
a significantly
improved existing product or service or process that will create or add value
for customers or workflow.
6.
The
start-up must not merely be engaged in:
o
developing
products or services or processes which do not have potential for
commercialisation; or
o
undifferentiated
products or services or processes; or
o
products or
services or processes with no or limited incremental value for customers or
workflow
7.
The
start-up must not be formed by splitting up, or reconstruction, of a business
already in existence.
8.
The
start-up has obtained certification from the Inter-Ministerial Board, setup by DIPP
to validate the innovative nature of the business, and
o
be supported by a
recommendation (with regard to innovative nature of business), in a format
specified by DIPP, from an incubator established in a post-graduate college in
India; or
o
be supported by an
incubator which is funded (in relation to the project) from GoI as part of any
specified scheme to promote innovation; or
o
be supported by a
recommendation (with regard to innovative nature of business), in a format
specified by DIPP, from an incubator recognized by GoI; or
o
be funded by an
Incubation Fund/Angel Fund/Private Equity Fund/Accelerator/Angel Network duly
registered with SEBI* that endorses innovative nature of the business; or
o
be funded by the
Government of India as part of any specified scheme to promote innovation; or
o
have a patent
granted by the Indian Patent and Trademark Office in areas affiliated with the
nature of business being promoted.
* DIPP may publish a negative list of funds which
are not eligible for this initiative.
START-UP INDIA
4) Registration of Start-up
Option
1:
An entity can register itself
through MCA or Registrar of Firms using the existing processes and subsequently
register itself on the Start-up India portal and mobile app as a Start-up to
avail the benefits.
Option
2:
An entity can register itself
through the Start-up India portal and mobile app using a seamless process. This
facility would be made available in the second phase of the Start-up India
portal and mobile app launch.
1.
Log in to Start-up India Portal
2.
Choose your legal entity
3.
Input your
incorporation/registration number
4.
Input your
incorporation/registration date
5.
Input PAN number (optional)
6.
Input your address with postal code
& state
7.
Input authorized representative
details
8.
Input director(s)/partner(s) details
9.
Choose and upload supporting
documents and self-certification
10.
Incorporation/registration
certificate of company/LLP/Partnership
11.
Registration to avail tax and IPR
12.
Certify the official notification
terms and conditions







